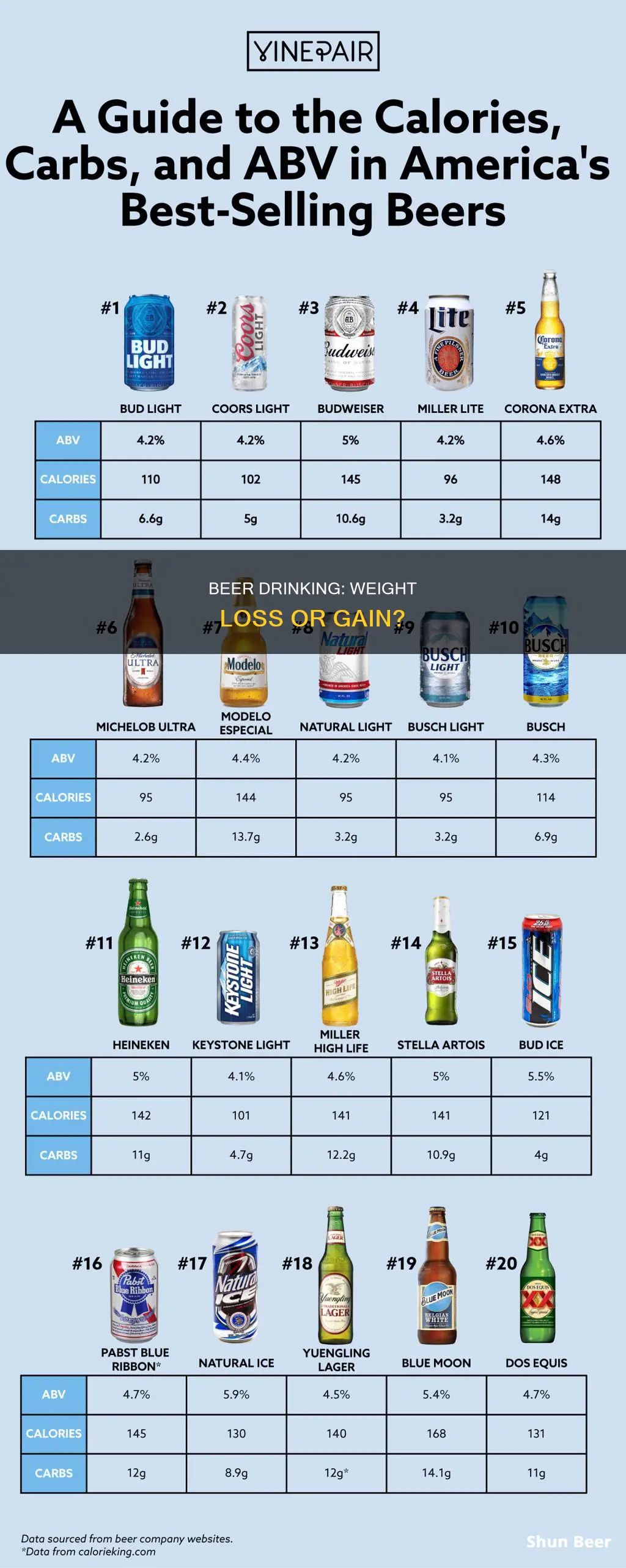
Beer and weight loss are not mutually exclusive, but it is challenging to lose weight while drinking beer. Beer can contribute a lot of calories, and it is metabolized differently by the body compared to other macronutrients like protein, carbs, and fat. The foundation of losing weight is to eat fewer calories than you burn, but beer provides calories without satisfying your hunger. One beer contains around 153 calories, and a craft beer can have even more, with some topping 200 calories. If you are trying to lose weight while still drinking beer, you will need to increase your exercise, change your diet, and monitor your alcohol consumption.
What You'll Learn
- Beer is an empty calorie drink, providing almost no nutrients
- Beer is a liquid, meaning calories are ingested quickly
- Alcohol is metabolised differently by the body, often halting fat-burning
- Beer affects sleep quality, which is linked to weight gain and muscle loss
- Beer reduces inhibitions, increasing the likelihood of overindulging in food

Beer is an empty calorie drink, providing almost no nutrients
Beer is often referred to as an "empty calorie" drink because it provides little to no micronutrients, fibre, or protein. In other words, while beer contains calories, it has low nutrient density, meaning there are few other nutrients relative to its energy content.
The term "empty calories" refers to calories from foods and beverages that are composed primarily or solely of calorie-rich macronutrients such as sugars and fats, but lack micronutrients, fibre, and protein. These empty calories can be difficult to fit into a balanced diet and can lead to an unhealthy diet and weight gain.
Beer, like other alcoholic beverages, falls into this category of empty calories. While beer may have had more nutritional value in the past, modern refining processes have stripped it of most nutrients. Today, beer contains a significant number of calories per pint, with the NHS claiming it has the same caloric content as a full-sized Mars Bar.
In addition to the high caloric content, beer can contribute to weight gain because alcohol reduces inhibitions and stimulates appetite. People often eat more when drinking, leading to increased calorie intake. Therefore, if one is trying to lose weight, it is important to consider not only the calories from beer but also the additional calories consumed due to increased appetite.
To fit beer into a healthy diet while trying to lose weight, one needs to be conscious of the calories ingested and make adjustments elsewhere in their diet or through increased physical activity. Switching to low-calorie or low-alcohol beers can also help reduce caloric intake without sacrificing the enjoyment of drinking beer.
Beer and an Upset Stomach: Should You Drink or Not?
You may want to see also

Beer is a liquid, meaning calories are ingested quickly
Beer is a liquid, and as such, it is easy to drink calories quickly. Beer is mostly water, but it also contains alcohol, which is metabolised by the body differently from other macronutrients. Beer is often referred to as "empty calories" because it provides almost no nutrients.
The calories in beer are ingested quickly because the liquid form means they do not need to be broken down during digestion. This is in contrast to solid foods, which require more time and energy to digest. As a result, drinking beer can lead to weight gain, especially if consumed in large quantities.
The speed at which calories are ingested also depends on the volume of beer consumed. For example, a 16-ounce bottle contains more calories than a 12-ounce can. Additionally, the alcohol content of the beer, expressed as a percentage of alcohol by volume (% ABV), will determine the caloric content. A higher ABV typically means higher calories.
To manage weight while drinking beer, it is important to be mindful of the calorie intake and make adjustments to eating habits. This may include reducing portion sizes, drinking less frequently, or choosing lower-calorie or lower-% ABV beers.
Ear Piercing and Beer: What's Safe?
You may want to see also

Alcohol is metabolised differently by the body, often halting fat-burning
Alcohol is metabolised differently by the body, and this often halts fat-burning. Alcohol is broken down in the liver by enzymes alcohol dehydrogenase (ADH) and aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH). ADH breaks down alcohol into acetaldehyde, and ALDH rapidly breaks down acetaldehyde into acetate. The acetate is further metabolised, and eventually leaves the body as carbon dioxide and water.
However, acetaldehyde is highly toxic and a known carcinogen. It can cause significant damage to the liver, pancreas, and brain, where it can also damage cells and tissues. Some researchers believe that acetaldehyde may be responsible for some of the behavioural and physiological effects attributed to alcohol, such as loss of judgment, decreased concentration, and impaired coordination.
In addition, alcohol is a nutrient and has a caloric value of about 7 kcal per gram. Unlike other nutrients such as carbohydrates, protein, and fat, alcohol is not stored and remains in body water until it is eliminated. This means that alcohol-derived calories are produced at the expense of the metabolism of normal nutrients.
Furthermore, alcohol interferes with fat burning by altering the NAD+/NADH redox ratio in the liver. This can inhibit the citric acid cycle, pyruvate dehydrogenase, and fatty acid oxidation, which are important for fat burning.
Finally, alcohol can increase appetite and stimulate your appetite, leading to increased calorie intake and making it more difficult to lose weight.
Mixing Beer and Hard Liquor: Safe or Not?
You may want to see also

Beer affects sleep quality, which is linked to weight gain and muscle loss
Beer and weight gain often go hand in hand, and if you enjoy drinking beer and eating calorie-rich food regularly, losing weight can be particularly difficult. According to a 2014 study in the American Journal of Public Health, alcohol consumption is related to not only weight gain but also obesity. Beer contains calories and carbohydrates, which can contribute to weight gain if consumed in excess.
In addition to its impact on weight, beer can also affect sleep quality. Alcohol is known to have a relaxing effect and can help people fall asleep more easily. However, excessive alcohol consumption is associated with poor sleep quality, including frequent nighttime and early morning awakenings. This can result in overall low-quality sleep and leave individuals feeling tired the next day.
The impact of beer on sleep quality is linked to weight gain and muscle loss. Poor sleep quality can lead to increased stress, fatigue, and mood disorders. Additionally, it raises the risk of obesity, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular disease. Sleep plays a crucial role in energy preservation, development, and growth. When sleep quality is compromised, the body's ability to regulate energy balance and support muscle growth and recovery may be affected.
It is important to note that non-alcoholic beer may have a different effect on sleep quality. Some studies suggest that the hops in non-alcoholic beer have a sedative effect, which can improve sleep quality. However, more research is needed to understand the specific impact of non-alcoholic beer on sleep and its potential benefits or drawbacks.
Beer Chillers: How Do They Work?
You may want to see also

Beer reduces inhibitions, increasing the likelihood of overindulging in food
Beer is a popular alcoholic drink, but it is important to remember that it is a drug that affects the body and can be addictive. Alcohol impacts the central nervous system, slowing it down and causing feelings of relaxation and lowered inhibitions. Beer contains calories, and regular drinking and eating calorie-rich food can lead to weight gain and even obesity.
Lowered inhibitions can also increase the likelihood of overindulging in food. Alcohol stimulates the appetite, and people often eat more when drinking. This is why many dieters choose to cut out alcohol completely when trying to lose weight. If you are trying to lose weight but still want to drink beer, it is important to be conscious of the calories you are consuming and to increase your exercise. It is also a good idea to prepare low-calorie snack options so that you can stay on track with your daily calorie intake.
In addition to the calories in beer, alcohol is a diuretic, which means it dehydrates you and can lead to hangovers. This can make you feel sluggish and less likely to exercise. To counteract this, it is recommended to drink one glass of water for every beer you consume.
Beer Goggles: The Science Behind Alcohol's Effect on Attraction
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
It is not advisable to try to lose weight by drinking beer. Beer is known to contribute a lot of calories, which can make it challenging for those trying to manage their weight. Beer is considered an "empty calorie" drink as it provides almost no nutrients.
The number of calories in a can of beer varies depending on the brand and type of beer. According to the USDA, a regular beer contains 153 calories, while a craft beer like Blue Moon can have up to 171 calories. Some craft beers can even exceed 200 calories.
If you want to lose weight while still drinking beer, you will need to make adjustments to your diet and exercise routine. You can try switching to light or low-percentage ABV beers, reducing your portion sizes, or drinking less frequently. It is also important to be mindful of the calories you are consuming and to increase your physical activity to create a caloric deficit.







