Quitting drinking is never easy, and there are two main options: quitting cold turkey or tapering off alcohol. Quitting cold turkey means stopping drinking all at once, without any period of adjustment or replacement therapy. While this method may be appealing to those who want a fresh start, it can be dangerous and is not recommended for people with alcohol dependence or a history of alcohol withdrawal. This is because the body goes into withdrawal, which can cause uncomfortable and even life-threatening symptoms. These include nausea, vomiting, shaking, headaches, insomnia, delirium tremens (DTs), high body temperature, convulsions, fever, hallucinations, and more. The severity and duration of these symptoms depend on several factors, such as the length of time one has been drinking, the amount consumed, overall health, and co-occurring medical or psychological issues.
Tapering off alcohol, on the other hand, involves slowly reducing alcohol consumption over time. This method gives the body time to adjust to life without alcohol and can help reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms. However, it can be challenging to taper off alcohol without professional help, and there is still a risk of relapse if done incorrectly.
Whether quitting cold turkey or tapering off, it is crucial to seek professional help and support throughout the process. Withdrawal from alcohol can be physically and psychologically strenuous, and having a strong support system in place is vital for a successful and safe recovery.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Difficulty | Quitting alcohol is difficult due to its social acceptance and widespread availability. |
| Danger | Quitting alcohol cold turkey can be dangerous as it can lead to withdrawal symptoms, including life-threatening ones such as seizures and delirium tremens (DTs). |
| Recommended Approach | It is not recommended to quit cold turkey. Gradually reducing alcohol consumption over time with the help of medication and medical monitoring is the safest approach. |
| Support | Seeking support from medical professionals, treatment centers, support groups, and peers is crucial for a successful and safe detox. |
| Withdrawal Symptoms | Withdrawal symptoms can range from mild to severe and include nausea, vomiting, shaking, headaches, insomnia, high body temperature, convulsions, and hallucinations. |
| Relapse | Quitting cold turkey increases the risk of relapse due to withdrawal symptoms and cravings. |
What You'll Learn

Alcohol withdrawal symptoms
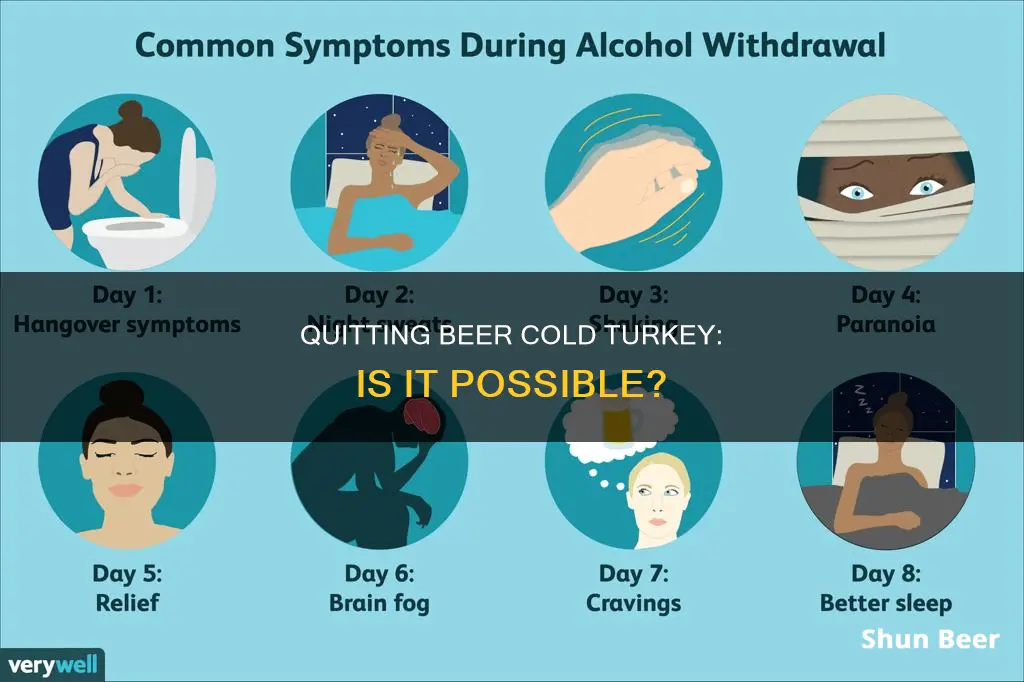
Quitting alcohol cold turkey can be dangerous, and alcohol is one of the few drugs with withdrawal symptoms that can lead to death. The symptoms of alcohol withdrawal can range from mild to severe, and they tend to occur within 8 hours to several days after the last drink. The severity of the symptoms depends on several factors, including the amount, frequency, and duration of alcohol consumption.
- 6-12 hours after the last drink: Mild symptoms such as insomnia, tremors, mild anxiety, stomachache, headache, excessive sweating, heart palpitations, and loss of appetite may occur.
- 12-24 hours after the last drink: Hallucinations may begin.
- 24-48 hours after the last drink: The risk of seizures is at its highest.
- 48-72 hours after the last drink: The risk for developing alcohol withdrawal delirium, also known as delirium tremens (DTs), continues. DTs is a severe form of alcohol withdrawal that can cause agitation, irritability, severe confusion, hallucinations, and cardiovascular disturbances.
It is important to note that those who have gone through alcohol withdrawal once are more likely to experience it again if they quit drinking in the future. Additionally, older adults, individuals with a history of alcohol withdrawal seizures, and those with physical or mental health conditions may be at a higher risk of experiencing more severe withdrawal symptoms.
If you or someone you know is experiencing alcohol withdrawal, it is important to seek medical help immediately, especially if there are severe symptoms such as seizures, hallucinations, fever, or irregular heartbeats. Treatment for alcohol withdrawal typically involves monitoring vital signs, providing fluids or medications through intravenous (IV) therapy, and administering sedatives until the withdrawal symptoms subside.
Beer and Metformin: Is Light Beer Safe?
You may want to see also

Risks of quitting cold turkey
Risks of Quitting Alcohol Cold Turkey
Quitting alcohol cold turkey can be dangerous and even life-threatening. Alcohol is one of the few drugs with withdrawal symptoms that can be severe and sometimes fatal. Here are some risks associated with quitting alcohol abruptly:
Cravings and Withdrawal
Quitting alcohol cold turkey can lead to intense cravings and debilitating withdrawal symptoms. The brain becomes rewired due to prolonged alcohol exposure and expects alcohol to function normally. When alcohol is suddenly removed, the brain and body struggle to stabilize, leading to cravings and withdrawal symptoms that can be challenging to manage.
Severe Withdrawal Symptoms
About half of individuals with an alcohol use disorder who quit cold turkey experience alcohol withdrawal syndrome (AWS). AWS can include symptoms such as high blood pressure, nausea and vomiting, seizures, delirium tremens (DTs), hallucinations, disorientation, rapid heart rate, fever, and sweating. In rare cases, AWS can lead to death.
Medical Complications
Heavy drinking can cause serious medical complications, including internal organ failure. Quitting cold turkey without medical supervision puts individuals at risk of developing life-threatening health problems involving the liver, heart, brain, and nervous system.
Relapse
Quitting alcohol cold turkey increases the risk of relapse due to a lack of accountability and support. The absence of a structured treatment plan and professional guidance makes it more challenging to maintain abstinence and prevents individuals from addressing the underlying causes of their addiction.
Serious Health Risks
Alcohol withdrawal can lead to dangerous health issues such as convulsions, seizures, gastric bleeding, and cardiac arrhythmia. Additionally, low electrolyte levels during withdrawal can cause cardiac complications, including arrhythmias and sudden death from a heart attack. Hypophosphatemia (low phosphate levels) can result in muscle weakness, coma, and respiratory failure.
Delirium Tremens (DTs)
DTs is a rare but severe form of alcohol withdrawal that can be fatal. It is commonly seen in individuals with a history of alcohol withdrawal, heavy drinkers, and those with a long-term alcohol addiction. Symptoms of DTs include seizures, hallucinations, confusion, sensitivity to light, nausea, and cardiovascular problems.
Beer and Gout: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Tapering off vs quitting cold turkey
If you are struggling with alcohol dependence or want to cut back on your alcohol consumption, there are two main options: quitting alcohol cold turkey or tapering off alcohol. Both methods involve quitting drinking, but tapering off involves reducing alcohol consumption gradually over time, while quitting cold turkey involves stopping alcohol consumption abruptly.
Pros and Cons of Tapering Off Alcohol
Tapering off alcohol is often considered a safer method of detoxing from alcohol, as it allows the body to gradually adjust to living without alcohol and can help reduce the intensity of withdrawal symptoms. It can also help individuals control cravings better and potentially lower the chance of relapse. However, tapering off alcohol can be difficult to do without professional support, and there is still a risk of relapse if it is not done correctly. Additionally, the tapering-off process may be slower than quitting cold turkey.
Pros and Cons of Quitting Cold Turkey
Quitting alcohol cold turkey may be the preferred option for those who do not have alcohol use disorder (AUD) or a history of alcohol withdrawal. It involves stopping alcohol consumption all at once, without any period of adjustment. While this method can be uncomfortable due to withdrawal symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, shaking, headaches, and insomnia, these symptoms are typically not life-threatening. However, quitting cold turkey without supervision increases the risk of relapse and binge drinking, which can lead to overdose.
The best way to safely quit drinking is by seeking professional advice from a doctor or treatment centre. They can help determine the most suitable method for your specific situation and provide information on managing withdrawal symptoms and psychological dependence on alcohol during the detox period.
Alcohol Withdrawal Symptoms and Risks
Alcohol withdrawal symptoms can range from mild to severe and may include increased blood pressure, nausea, vomiting, shaking, headaches, insomnia, hallucinations, fever, tremors, confusion, seizures, and disturbances in the cardiovascular system. In severe cases, alcohol withdrawal can lead to alcohol withdrawal syndrome, which includes delirium tremens ("DTs") and can be fatal. Therefore, it is crucial to seek professional guidance when considering quitting alcohol to ensure a safe and effective detox process.
Morphine and Beer: A Dangerous Mix?
You may want to see also

Getting help
Quitting alcohol can be challenging, and it's important to seek professional help to ensure a safe and successful recovery. Here are some steps and resources to consider when seeking help for alcohol dependence:
- Consult a medical professional: Speak to your doctor or a healthcare provider about your drinking habits and desire to quit. They can assess your level of alcohol dependence and provide guidance on the best course of action. Be honest about your drinking history and any physical or psychological issues you may be experiencing.
- Detoxification (Detox): Undergoing detoxification in a medical facility or treatment centre is often the first step in the recovery process. This involves safely managing the withdrawal symptoms and helping your body adjust to functioning without alcohol. Medical professionals will monitor your vital signs, treat withdrawal symptoms, and provide emotional support.
- Medication: Doctors may prescribe medications to ease withdrawal symptoms, curb cravings, and prevent life-threatening complications. These can include benzodiazepines and other tapering drugs.
- Therapy and Counselling: Behavioural therapies, such as cognitive-behavioural therapy (CBT) and dialectical behaviour therapy (DBT), can help address the underlying causes of addiction and provide you with healthy coping mechanisms. Counselling sessions with a trained therapist can also help you process your thoughts and emotions during recovery.
- Support Groups: Joining support groups, such as Alcoholics Anonymous (AA), can provide a sense of community and accountability during your journey. These groups offer meetings, both in-person and virtual, where individuals can share their experiences, provide mutual support, and learn from one another.
- Substance Use Treatment Programs: After detoxification, it is crucial to continue your recovery journey by attending a substance use treatment program. These programs can help you develop healthy coping skills and address the reasons behind your alcohol abuse. They may include individual or group therapy, counselling, and participation in mutual-help groups.
- Address Co-occurring Disorders: If you have co-occurring mental health or medical conditions, ensure that these are addressed as part of your treatment plan. Treating any underlying issues is essential for long-term recovery.
- Relapse Prevention: Relapse is a common challenge during recovery. Work with your treatment team to develop a relapse prevention plan that includes identifying triggers, developing healthy coping strategies, and seeking ongoing support.
- Follow-up Care: Recovery is an ongoing process, and it's important to maintain a connection with your healthcare providers even after completing a treatment program. Regular check-ins can help monitor your progress, address any challenges, and provide additional support as needed.
Remember, seeking professional help is crucial when quitting alcohol, especially if you have a history of alcohol dependence or withdrawal symptoms. The support and guidance of medical professionals can make a significant difference in your recovery journey, ensuring your safety and long-term sobriety.
Beer and Aimovig: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Benefits of quitting
Quitting drinking cold turkey can be dangerous, and it is not recommended due to the risk of severe and potentially life-threatening withdrawal symptoms. However, quitting drinking safely can bring about numerous benefits to your physical and mental health.
Improved Sleep
Alcohol disrupts the important REM stage of sleep and may interfere with your breathing and cause you to wake up multiple times during the night. Quitting drinking can lead to more restful sleep, improving your productivity, cognitive function, emotional regulation, and behaviour.
Better Hydration
Alcohol is a diuretic, causing dehydration, which can lead to headaches, fatigue, and decreased motivation. By quitting drinking, you will be better hydrated, which has a range of benefits, including fewer headaches, improved mood and concentration, and more radiant skin.
Weight Loss
Alcohol is high in calories and can increase your appetite and impulsivity, leading to weight gain. Quitting drinking can help you lose weight by reducing your calorie intake and improving your ability to make healthier food choices.
Lower Blood Pressure
Heavy drinking can cause an increase in blood pressure, which is a major risk factor for heart disease. Quitting drinking can help lower your blood pressure, reducing the risk of future health problems.
Improved Liver Function
The liver is responsible for filtering toxins from the body, and alcohol is particularly toxic to cells. Quitting drinking allows the liver to repair itself and regenerate, improving its function and contributing to better skin health.
Enhanced Cognition
Alcohol can impair cognitive function, making it difficult to think clearly and remember things. Quitting drinking can lead to improvements in memory, perception, and motor skills, enhancing your overall cognitive abilities.
Better Relationships
Excessive drinking can lead to unhealthy habits and contribute to conditions like alcohol use disorder. Quitting drinking can help you focus on your relationships, improve your mood, and boost your self-esteem, leading to more fulfilling connections with others.
Reduced Cancer Risk
While the link is still being studied, there is evidence that heavy drinking increases the risk of several types of cancer. Quitting drinking may lower your chances of developing these cancers, improving your long-term health outcomes.
Improved Sex Life
While a small amount of alcohol may enhance couples' intimacy, excessive drinking can have the opposite effect, causing sexual dysfunction in both men and women. Reducing alcohol intake can improve sexual desire and performance, leading to a more fulfilling sex life.
Fewer Accidents and Injuries
Alcohol plays a significant role in accidents, injuries, and deaths from various causes, including trauma, burns, drownings, and homicides. Quitting drinking or even reducing your alcohol intake can significantly lower the risk of accidents and injuries, improving your overall safety.
Drinking Beer and Driving in Mississippi: What's Allowed?
You may want to see also







