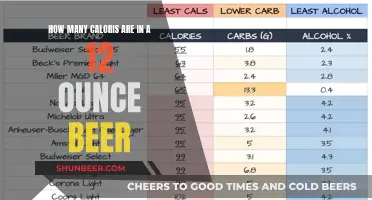
Beer is notoriously high in calories and carbs, with a pint of 5% ABV beer containing around 240 calories. However, in recent years, the beer scene has diversified, and there are now many low-calorie options available. Non-alcoholic beers, for example, tend to be lower in calories than their alcoholic counterparts because alcohol contains around 56 calories per unit. However, non-alcoholic beers often contain added sugar to improve the flavour, so they may not always be a healthier option. When it comes to alcoholic beers, lagers are the most popular low-calorie option, with Budweiser Select (2.4% ABV) containing just 55 calories per 354 ml, and Coors Light (4.2% ABV) containing 102 calories per 350 ml. For those who prefer ales, Le Petit Prince (2.9% ABV) contains just 75 calories per 354 ml, while Guinness, a classic Irish stout, has only 126 calories and 4.2% alcohol per 350 ml. So, if you're watching your waistline, you don't have to give up beer completely – there are plenty of low-calorie options to choose from.
What You'll Learn

Low-calorie beers
Beer is typically high in calories, but the good news is that there are now many low-calorie options available. These beers have fewer carbohydrates and a lower alcohol content, resulting in a reduced calorie count.
Lagers
Lagers are the most popular type of beer. They are known for their crisp, light, and clean taste. Here are some low-calorie options:
- Budweiser Select (2.4% ABV, 55 calories)
- Molson Ultra (3% ABV, 70 calories)
- Sleeman Light (4% ABV, 90 calories)
- Amstel Light (4% ABV, 95 calories)
- Miller Light (4.2% ABV, 96 calories)
- Heineken Light (4.2% ABV, 97 calories)
- Corona Light (3.7% ABV, 99 calories)
- Coors Light (4.2% ABV, 102 calories)
- Bud Light (4.2% ABV, 103 calories)
Ales
Ales are produced in colder countries such as Canada, Germany, and Belgium and are known for their fruity and bitter taste. Here are some low-calorie options:
- Le Petit Prince (2.9% ABV, 75 calories)
- Dogfish Head Slighty Mighty (4% ABV, 95 calories)
- Lagunitas DayTime (4% ABV, 98 calories)
- Kona Kanaha Blonde Ale (4.2% ABV, 99 calories)
- Harpoon Rec League (3.8% ABV, 120 calories)
- Fat Tire Amber Ale (5.2% ABV, 160 calories)
Stouts
Stouts are a type of ale that use roasted barley to create a rich, dark colour. Here are some low-calorie options:
- Guinness Extra (5.6% ABV, 126 calories)
- Young’s Double Chocolate Stout (5.2% ABV, 150 calories)
- Samuel Smith Oatmeal Stout (5% ABV, 190 calories)
Gluten-Free Beers
Gluten-free beers are made from grains like millet, sorghum, and rice, and are suitable for those following a gluten-free diet. Here are some low-calorie options:
- Glutenberg Blonde (4.5% ABV, 160 calories)
- Green’s IPA (6% ABV, 160 calories)
- Coors Peak (4.7% ABV, 170 calories)
Non-Alcoholic Beers
Non-alcoholic beers are great for those who want to avoid alcohol but still enjoy a cold beverage. Here are some low-calorie options:
- Coors Edge (0.5% ABV, 45 calories)
- Heineken 0.0 (0.0% ABV, 69 calories)
- Bavaria 0.0% Beer (0.0% ABV, 85 calories)
- Heineken 0.0 (0.0% ABV): 69 calories
Other Low-Calorie Options
In addition to the beers mentioned above, here are some other low-calorie options:
- Tennents Light Lager
- Marstons Resolution Ale
- Favela Organic & GF Lager
- Budweiser Prohibition Brew (0.0% ABV, 150 calories)
- Michelob Ultra Pure Gold (85 calories)
- Miller Lite
Spent Grain Pretzel Sticks: Calorie Conundrum?
You may want to see also

Alcohol-free beers
- Coors Edge (0.5% ABV): 45 calories
- Becks Non-Alcoholic Beer (0.0% ABV): 60 calories
- Heineken 0.0 (0.0% ABV): 69 calories
- Bavaria 0.0% Beer (0.0% ABV): 85 calories
- Budweiser Prohibition Brew (0.0% ABV): 150 calories
- Heineken 0.0 (0.0% ABV): Heineken 0.0 is a non-alcoholic beer that tastes impressively similar to the original Heineken, with refreshingly fruity notes.
- Beavertown Lazer Crush (0.0% ABV): This non-alcoholic IPA from Beavertown has a special kind of yeast that ferments malt without producing alcohol. It has a sweet and juicy taste with notes of apple and caramel and a light, peachy aftertaste.
- Erdinger Alkoholfrei (0.0% ABV): This isotonic beer is slightly salty on the lips with a fresh-baked bread taste that goes well with German dishes or a Greek salad. It has a pleasant sherbet fragrance and a deep, lacy froth.
- Days Pale Ale (0.0% ABV): This complex and refreshing pale ale from Edinburgh brewer Days has hints of mango and plum, with gingerbread, caramel and malted milk depths that linger on the tongue.
- Lucky Saint (0.5% ABV): This slightly cloudy Bavarian lager has a golden body, a good foamy head, and a slight salty-sweetness with floral and citrus notes.
- Estrella Galicia (0.0% ABV): This zero-alcohol lager stands out among its big-name competitors with its zingy, sparkly, and slightly salty-sweet taste.
Organic Beer Calories: How Much Energy Do They Provide?
You may want to see also

Beer and weight loss
The short answer is yes, you can drink beer and still lose weight. However, it depends on various factors, including the type of beer, the quantity consumed, and your overall diet and exercise regimen. Beer is often associated with weight gain, especially around the belly, due to its relatively high calorie content. A standard pint of 5% ABV beer contains around 240 calories, similar to a slice of pizza. Additionally, beer is one of the highest carb alcoholic drinks, with regular beers containing over 14 grams of carbs per can.
Low-calorie beers
To cater to the growing demand for lower-calorie options, breweries have introduced low-calorie beers that provide a refreshing alternative without compromising on flavour. These beers typically have 35% fewer calories than regular lager, making them suitable for those on a low-carb diet. Examples include Tennents Light Lager, Skinny Brands Beer, Coors Light, and Budweiser Select.
Non-alcoholic beers
Non-alcoholic beers are also lower in calories since alcohol itself is high in calories, containing 7 calories per gram. However, it's important to note that non-alcoholic beers often have added sugar to improve flavour, resulting in a higher carbohydrate and sugar content. Therefore, they may not be suitable for those on a low-carb or low-sugar diet. Examples of non-alcoholic, low-calorie beers include Coors Edge, Beck's Non-Alcoholic Beer, Heineken 0.0, and Bavaria 0.0% Beer.
Calorie comparison
When comparing alcoholic and non-alcoholic beers, it's important to consider the overall calorie intake. For example, a 330ml bottle of Carlsberg (3.8%) has 122 calories, while a 330ml bottle of Carlsberg "0.0" (0%) has 73 calories. However, a non-alcoholic beer like Peroni Libera Alcohol Free contains around 10 grams of sugar, which quickly adds up if you're not careful.
Alcohol and weight loss
While alcohol is not inherently healthy, giving it up completely is not necessary for weight loss. Alcoholic beverages can be a key part of socialising, and low-calorie beers provide a great alternative to higher-calorie drinks like cocktails and wine. However, it's important to remember that low-calorie beers may still be high in alcohol, so moderation is key. Enjoying a drink occasionally without overindulging can be part of a balanced lifestyle.
Tips for drinking beer while losing weight
- Opt for low-calorie or low-sugar beers.
- Practice moderation and stick to 1-2 drinks per day.
- Be mindful of the overall calorie intake, including any extra snacks consumed while drinking.
- Choose non-alcoholic beers for a lower-calorie option, but watch out for added sugar.
- Pair spirits like whisky, gin, or tequila with soda water and fresh lime juice for a lower-calorie alternative.
Light Beer Calories: Miller's Low-Cal Brew
You may want to see also

Beer and sugar content
Beer is made from yeast, grains, spices, and water. Sugar is not typically listed as an ingredient in beer, but it is created naturally when grains are processed and fermented by yeast. This process is called beer gravity, referring to the density of the liquid extracted from the mashing process during the brewing of beer, known as the wort. When the wort has a lot of sugar, it's called a high gravity wort.
Once yeast is added to the wort, the sugar content decreases while the alcohol content increases. After fermentation, beer is typically made up of 80% fermentable sugars and 20% oligosaccharides, a type of carbohydrate.
The final sugar content of a beer depends on several factors, including its gravity, the type of yeast used, and any additional flavours included, such as honey or corn syrup.
The amount of sugar in beer varies depending on the type and brand. Generally, beer has less sugar than other alcoholic drinks like wine. However, some beers can have a higher sugar content due to added ingredients.
The exact amount of sugar in beer can be difficult to pinpoint as it is not required by law to be labelled. However, according to Healthline, here is the carb and sugar content for some of the most popular beers in America:
- Bud Light: 4.6 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Budweiser: 10.6 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Busch: 6.9 grams of carbs, no sugar reported
- Busch Light: 3.2 grams of carbs, no sugar reported
- Coors Banquet: 11.7 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Coors Light: 5 grams of carbs, 1 gram of sugar
- Coors Non-alcoholic: 12.2 grams of carbs, 8 grams of sugar
- Heineken: 11.4 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Miller High Life: 12.2 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Miller Lite: 3.2 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Regular beer: 12.8 grams of carbs, 0 grams of sugar
- Light beer: 5.9 grams of carbs, 0.3 grams of sugar
- Non-alcoholic beer: 28.5 grams of carbs, 28.5 grams of sugar
It is important to note that non-alcoholic beers tend to have a very high sugar content, while light beers generally have more sugar than regular beers. Additionally, the more carbs a beer has, the higher the sugar content.
Beer and Health
The sugar content in beer is generally very low, so beer drinkers don't need to be overly concerned about their sugar intake from this source. However, beer can still significantly affect blood sugar levels. Like other alcoholic drinks, beer will cause a sudden drop in blood sugar for up to 24 hours after consumption. Since it competes with the liver for glucose production, drinking beer will result in low blood sugar the next day. This, paired with impaired judgment, can cause issues with blood sugar control.
For people with diabetes, it is important to practice moderation when drinking beer. While one to two cans of beer can be beneficial for diabetic people, consuming large amounts can have certain risks. Consistently consuming high-sugar and high-carb beverages like beer can lead to spikes in blood sugar levels, increasing the risk of developing type 2 diabetes or other blood sugar-related issues.
Low-Sugar and Sugar-Free Beer Options
There are options for reduced-sugar beers, including non-alcoholic, low-carb, and light beer varieties. Some examples of low-carb beers include:
- Michelob Ultra: 2.6 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Corona Premier: 2.6 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Budweiser Select 55: 1.9 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Beck’s Premier Light: 3.8 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Miller Lite: 3.2 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Amstel Light: 5 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
- Heineken Light: 6 grams of carbs per 12 fl oz serving
Calories in Kingfisher Beer: Nutritional Facts for Beer Enthusiasts
You may want to see also

Beer and carbohydrates
Beer is made by fermenting grains such as barley and wheat, which contain carbohydrates. Most beers also contain added sugars, which further increase the carbohydrate content of the beverage. The number of grains and added sugars that remain in the beer depends on the fermentation process.
The amount of carbohydrates in beer varies according to the ingredients and overall sugar levels. In general, light beers contain fewer carbohydrates than full-flavoured beers. A 12-ounce serving of Amstel Light, for example, contains 5.3 grams of carbohydrates, while a 12-ounce serving of Budweiser contains 10.6 grams.
Beer is typically one of the highest-carb alcoholic drinks available. A regular beer can contain upwards of 14 grams of carbohydrates per can, and a pint of beer typically contains 10-15 grams of carbohydrates. A medium-strength lager is a good option for those looking to minimise their carb intake, as it will tend to have 8-12 grams of carbohydrates.
Low-carb beers are available for those who want to enjoy a beer while watching their waistline. These beers can contain as few as 0.7 grams of carbohydrates per bottle.
Calories in Old Milwaukee Beer: Nutritional Breakdown
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A low-calorie beer typically has fewer than 150 calories per serving.
Yes, non-alcoholic beers are usually lower in calories than regular beers. However, they often contain added sugar to improve the taste, so they may not be suitable for low-carb or low-sugar diets.
Yes, there are many low-calorie beers that are said to taste good, including:
- Budweiser Select
- Coors Light
- Corona Light
- Miller Light
- Heineken Light
- Corona Extra
- Skinny Brands Beer
- Guinness
- Brooklyn Pilsner Lager Beer
- Budweiser
- Big Drop Brewing Co. Paradiso Citra IPA
Yes, some examples of low-calorie, non-alcoholic beers include:
- Coors Edge
- Beck's Non-Alcoholic Beer
- Heineken 0.0
- Bavaria 0.0% Beer
- Budweiser Prohibition Brew