Ginger beer is a popular drink, often used as a mixer for cocktails and mocktails. It is also a good option for those seeking health benefits from ginger. While ginger beer is not a low-calorie drink, there are many low-calorie options available on the market. These include sugar-free and diet ginger beers, which tend to be sweetened with alternative sweeteners such as erythritol, stevia, monk fruit, or aspartame. Some popular low-calorie ginger beer brands include Fever-Tree, Regatta, Barritt's, Gosling's, and Zevia.
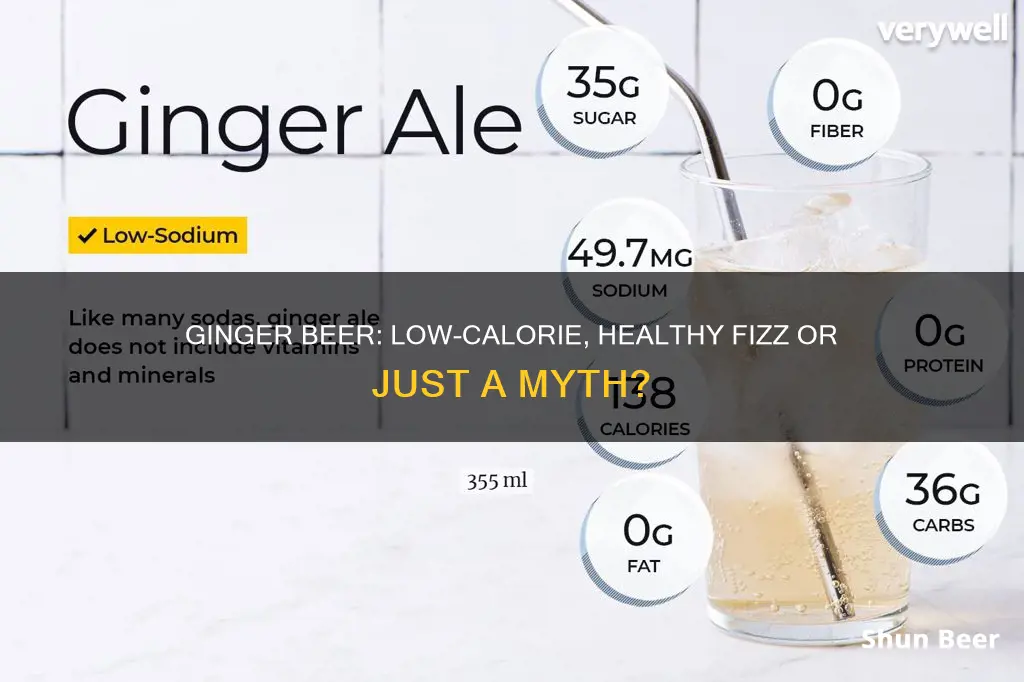
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Calories | 0-170 |
| Fat | 0-0.5 g |
| Carbohydrates | 2-40 g |
| Sugar | 0-40 g |
| Sodium | 0-41 mg |
| Fiber | 0 g |
| Protein | 0-1 g |
What You'll Learn

Ginger beer vs ginger ale
Ginger beer and ginger ale are two drinks with a lot of similarities, but also some key differences. Both are fizzy ginger drinks with a rightful place behind any bar, and both can be used in cocktails. However, ginger beer tends to be the more dominant flavour in cocktails, whereas ginger ale has a more delicate flavour profile and takes a back seat to the drink's other elements.
Origins
The history of ginger beer is a little murky. While many tie its origins to 18th-century England, the drink is likely much older. Early iterations were fermented, resulting in an alcoholic drink with an ABV of around 11%. Today, most ginger beers contain only trace amounts of alcohol (less than 0.5% ABV). Modern producers add carbon dioxide for forced carbonation, though some small-batch producers may use brewer's yeast to develop the bubbles.
The origins of ginger ale are much more recent. In 1866, Detroit-based pharmacist James Vernor started selling his version, making Vernor's Ginger Ale one of the oldest soft drinks in America. It's said that Vernor mixed tonic water with vanilla, spices, and ginger; then stored the mixture in an oak barrel, where it remained for a few years while he went to fight in the Civil War. Upon returning, he discovered his concoction: a golden ale, sweet and pungent in its ginger flavour, with an "aged" depth.
Ingredients and Flavour
Fresh ginger gives ginger beer its characteristic bright, bold, and spicy flavour profile. It's often a dominant flavour in cocktails like a Moscow Mule or Dark and Stormy.
Ginger ales tend to have a much more delicate flavour profile. To make ginger ale at home, you need little more than a ginger-flavoured simple syrup and carbonated water. Commercial brands may swap in "natural flavours", a byproduct the FDA defines as:
> "essential oil, oleoresin, essence or extractive, protein hydrolysate, distillate, or any product of roasting, heating or enzymolysis, which contains the flavouring constituents derived from [...] root, leaf, or similar plant material…"
Health Benefits
While ginger root has all kinds of health benefits, not all ginger beverages are made with real ginger, so mileage may vary by brand. If you're shopping for a ginger drink to settle an upset stomach, choose ginger beer, which is more likely to use fresh ginger in the brewing process and is, thus, better suited to relieve nausea or an upset stomach.
St. Pauli N.A. Beer: How Many Calories?
You may want to see also

Low-calorie options
If you're looking for a ginger beer that's low in calories, there are several options available. Here are some popular choices:
Fever-Tree Refreshingly Light Ginger Beer
Fever-Tree's Refreshingly Light Ginger Beer is a popular choice among those looking for a low-calorie option. It has a strong ginger flavour and is crafted with a blend of three different types of ginger from the Ivory Coast, Nigeria, and Cochin, India. This drink is also non-alcoholic and has only 38 calories per 6.8 fl. oz. bottle.
Reed's Zero Sugar EXTRA Ginger Beer
Reed's Zero Sugar EXTRA Ginger Beer is another great option, especially if you're looking for a sugar-free and calorie-free beverage. It is sweetened with erythritol, stevia, and monk fruit, and it contains a high amount of real ginger. This drink is also a good choice if you want to reap the functional benefits that ginger provides.
Barritt's Sugar-Free Diet Ginger Beer
Barritt's Sugar-Free Diet Ginger Beer is a solid sugar-free and low-calorie option. It still has a spicy and very gingery flavour, making it a great choice for mixed drinks or Moscow mules.
Q Mixers Light Ginger Beer
Q Mixers Light Ginger Beer is a premium cocktail mixer made with real ingredients. It has only 40 calories per can and is a good option if you're looking for a lighter ginger beer without sacrificing flavour.
Zevia Zero Calorie Ginger Root Beer
Zevia offers a zero-calorie and sugar-free ginger beer that is sweetened with stevia. While it may not have the same level of ginger flavour as some of the other options, it can be a good choice if you're looking for a low-calorie alternative.
Regatta Light Ginger Beer
Regatta Light Ginger Beer is another option for those looking for a lighter and less spicy ginger beer. It has a mellow flavour with less burn and no lingering finish, making it similar to a ginger ale. It contains 13 grams of sugar and is a good choice if you're looking for something sweet but not too sweet.
Calorie-Rich Tripel Beer: How Many Calories in One?
You may want to see also

High sugar content in ginger beer
Ginger beer is often loaded with sugar, with some brands containing up to 40 grams of sugar per serving. This is significantly higher than the recommended daily sugar intake, which is around 25 grams for women and 36 grams for men, according to the American Heart Association.
While ginger root has many health benefits, most ginger beers are essentially just regular soda. However, some ginger beers are better for you than others. Dietitian Suzanne Dixon recommends looking for ginger beers with more natural ginger, as this is generally associated with lower sugar content. She also suggests choosing cloudy beers with visible pieces of ginger, as these tend to have less added sugar.
Some ginger beers, such as Reed's Zero Sugar Extra Ginger Beer and Barritt's Sugar-Free Diet Ginger Beer, are sweetened with alternative sweeteners like erythritol, stevia, and monk fruit, resulting in zero-calorie beverages. However, these drinks may have a different taste profile than traditional ginger beer due to the absence of sugar.
Even among regular ginger beers, the sugar content can vary significantly. For example, Fever-Tree Refreshingly Light Ginger Beer contains 8 grams of sugar per serving, while Regatta Light Ginger Beer contains 13 grams, and Pennyback Ginger Beer contains a whopping 27 grams. Therefore, it is essential to read the nutrition labels and choose ginger beers with lower sugar content if you are concerned about your sugar intake.
Calories in Fat Head's Bumble Berry Beer: Nutritional Breakdown
You may want to see also

Health benefits of ginger
Ginger has a long history of use in various forms of traditional and alternative medicine. It is used to add flavour to sweet and savoury foods and has a range of health benefits. Here are some of the health benefits of ginger:
Nausea Relief
Ginger is well-known for its ability to relieve nausea and vomiting, especially during pregnancy. It can also help with chemotherapy-related nausea and seasickness.
Improved Digestion
Ginger encourages efficient digestion by speeding up the rate at which food exits the stomach and continues through the digestive process. It can help with bloating, gas, and constipation.
Antibacterial and Antiviral Properties
The active compounds in ginger, called gingerols, have antibacterial properties that can help keep your mouth healthy and prevent periodontal disease. Additionally, certain chemical compounds in fresh ginger can help ward off germs and halt the growth of harmful bacteria like E. coli and shigella.
Anti-inflammatory Properties
Ginger contains over 400 natural compounds, some of which have anti-inflammatory effects. This may be helpful in treating symptoms of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis.
May Lower Blood Sugar
Some studies suggest that ginger may have anti-diabetic properties and can help lower blood sugar levels in people with type 2 diabetes.
May Reduce Menstrual Pain
Ginger has been found to be effective in reducing dysmenorrhea or menstrual pain. In studies, women who took ginger powder during their cycle experienced less pain compared to those who didn't.
May Lower Cholesterol
Consuming ginger has been linked to reduced triglycerides and LDL ("bad") cholesterol levels, while increasing HDL ("good") cholesterol.
May Reduce Cancer Risk
The gingerol and other antioxidant and anti-inflammatory compounds in ginger may help reduce the risk of certain types of cancer, such as colorectal, pancreatic, and liver cancer.
May Improve Brain Function
Compounds in ginger, such as 6-shogaol and 6-gingerol, may help prevent degenerative brain diseases like Alzheimer's, Parkinson's, and multiple sclerosis.
While ginger has many potential health benefits, it is important to consume it in moderation. Large doses of ginger may cause abdominal discomfort and mouth and throat irritation in some individuals. Additionally, while generally safe during pregnancy, it is always best to consult a healthcare professional before consuming ginger if you are pregnant or breastfeeding.
Calories in Sierra Nevada Beer: What's the Count?
You may want to see also

Natural vs artificial sweeteners
Ginger beer is a popular drink, but it is essentially a soda, and so it is often loaded with sugar. However, there are many sugar-free and low-calorie options available. These sugar-free options are often sweetened with artificial sweeteners.
There are pros and cons to both natural and artificial sweeteners, and it is important to understand the differences between the two.
Natural sweeteners include honey, agave nectar, maple syrup, and stevia. These are considered more natural and unprocessed than table sugar, but they are still classed as added sugars and undergo some form of processing. They are also broken down into glucose and fructose during digestion, just like table sugar, and there is no evidence that they are any better for you. However, they may contain small amounts of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals, and some are used for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, or antibacterial effects.
Artificial sweeteners are synthetic sugar substitutes and are often many times sweeter than real sugar. They include aspartame, saccharin, and sucralose. These are zero-calorie sweeteners and are found in many "sugar-free" products. While they are generally safe to consume in moderation, there have been some studies that found links between artificial sweeteners and cancer.
So, which is better? Well, the majority of your diet should consist of foods and beverages without added sweeteners. However, if you are looking for a sweetener to use in moderation, natural sweeteners may be a better option as they can provide some additional health benefits. But remember, they are still a form of added sugar and can contribute to weight gain and associated health risks if consumed in excess.
Calories in Carlsberg Beer: Nutritional Facts and Figures
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
It depends on the brand. Some ginger beers are low calorie, such as Barritt's Sugar Free Diet Ginger Beer, while others are not.
Some low-calorie ginger beer options include Fever-Tree Refreshingly Light Ginger Beer, Reed's Zero Sugar Extra Ginger Beer, and Q Mixers Light Ginger Beer.
If you are making a Moscow Mule at home, you can use a combination of diet ginger beer and club soda, or you can make your own ginger beer using ginger juice, fresh-pressed ginger, and other ingredients.







