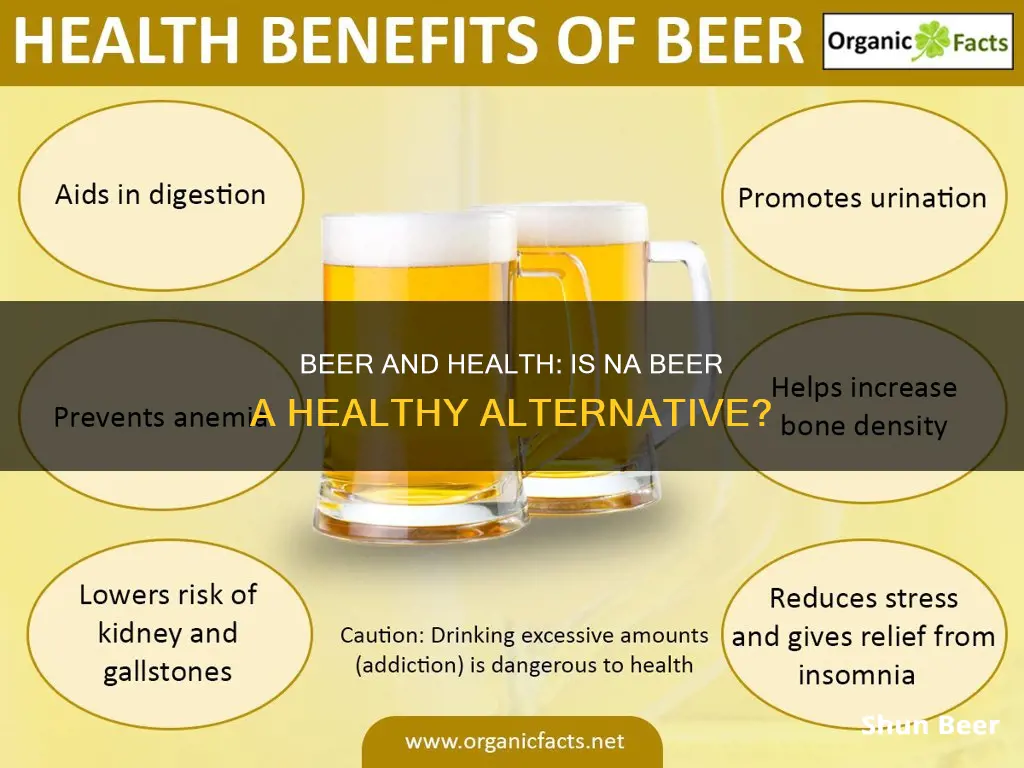
Non-alcoholic beer has been gaining popularity in recent years, with people becoming more aware of the physical and mental benefits of an alcohol-free lifestyle. But is it actually healthy?
Non-alcoholic beer is often presented as a safe alternative to alcoholic beer, and it's true that it can be beneficial for certain people. For example, it can be a good option for those looking to cut back on their alcohol intake, as it satisfies your taste buds without the buzz. It also tends to be lower in calories than regular beer. However, it's important to remember that non-alcoholic beer still contains calories and carbohydrates, so it's not necessarily a healthy choice.
There are also some potential risks associated with non-alcoholic beer. For pregnant people or those trying to become pregnant, it's best to avoid non-alcoholic beers as they may still contain small amounts of alcohol. Additionally, for people recovering from alcohol use disorder, the smell and taste of non-alcoholic beer may serve as a trigger and lead to a relapse.
So, while non-alcoholic beer can be a healthier alternative to regular beer in some ways, it's not necessarily a health food and should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced lifestyle.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Calories | Fewer calories than regular beer |
| Carbohydrates | More carbs than regular beer |
| Sugar | No added sugar |
| Vitamins | Contains B vitamins |
| Minerals | Contains calcium, potassium, zinc, selenium, and iron |
| Antioxidants | Contains phenols |
| Fiber | Contains fiber |
| Electrolytes | Contains electrolytes |
| Silicon | Contains high amounts of silicon |
| Alcohol | Up to 0.5% alcohol by volume (ABV) |
| Sleep | May improve sleep quality |
| Stress | May help reduce stress |
| Circulation | May improve circulation |
What You'll Learn

Non-alcoholic beer is a healthier alternative to regular beer
Non-Alcoholic Beer: A Healthier Alternative to Regular Beer
Non-alcoholic beer has come a long way from its early days of being a tasteless, watered-down version of traditional beer. Now, with the ever-expanding craft beer scene, non-alcoholic options have improved in taste and become more popular. But is non-alcoholic beer healthier than regular beer?
Fewer Calories and Less Alcohol
Non-alcoholic beer typically has fewer calories than regular beer. Alcohol contains 7 calories per gram, and many commercial beers range from 140 to 170 calories, while non-alcoholic beers usually range from 17 to 90 calories. Additionally, non-alcoholic beers may have slightly fewer carbohydrates.
Most importantly, non-alcoholic beers contain little to no alcohol. By definition, non-alcoholic beers can have up to 0.5% alcohol by volume (ABV), while alcohol-free beers contain 0.0% ABV. In comparison, a typical light beer contains 3.2% ABV. Alcohol is a toxin, and reducing alcohol intake can lower the risk of chronic diseases and improve mental health.
Vitamins, Minerals, and Antioxidants
Non-alcoholic beer contains essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, including B vitamins, calcium, potassium, zinc, selenium, and iron. These nutrients can have various health benefits.
Hydration and Bone Density
Non-alcoholic beer can be a good source of hydration, outperforming even water in this regard. A study on male soccer players found that drinking around 23 ounces of non-alcoholic beer before exercise maintained hydration better than water. Additionally, non-alcoholic beer contains high amounts of silicon, which boosts collagen production, leading to healthier bones, blood vessels, hair, skin, and nails.
Sleep, Stress Reduction, and Improved Circulation
Non-alcoholic beer can promote better sleep by helping individuals fall into a deep and restful slumber. It may also reduce stress and anxiety, with studies showing that drinking around 11 ounces of non-alcoholic beer per night for two weeks can help lower stress levels. Furthermore, the phenols in non-alcoholic beer can improve blood circulation and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease and atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries).
A Word of Caution
While non-alcoholic beer offers these health benefits, it is still not a completely healthy beverage. It contains empty calories and carbohydrates, and it should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet. Additionally, pregnant individuals and those recovering from alcohol use disorders should avoid non-alcoholic beers due to the small amount of alcohol they may contain.
In conclusion, non-alcoholic beer is a healthier alternative to regular beer. It provides several health benefits, including improved hydration, bone density, sleep, and reduced stress and cardiovascular risk. However, it should be consumed in moderation and may not be suitable for certain populations.
Hard Seltzer vs Beer: Which Drink is Healthier?
You may want to see also

It contains essential vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants
Beer is made from natural ingredients, including malted cereals (most often barley), hops, yeast, and water. Thanks to these ingredients, beer contains essential vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants that can positively contribute to a person's diet.
Beer contains small amounts of B vitamins from the cereal and yeast, and fibre and polyphenols from the cereals and hops. B vitamins are essential for maintaining healthy nerve cells, producing red blood cells, and getting energy from food. Polyphenols are a type of antioxidant that can help protect the body against disease and damage caused by free radicals.
The specific antioxidants in beer are different from those in wine because the barley and hops used in beer production contain different flavonoids from those in the grapes used in wine production. Beer also contains more protein and B vitamins than wine.
The amount and type of vitamins, minerals, fibre, and antioxidants in beer can vary depending on the raw materials used and the brewing process. For example, beers made from barley tend to contain more silicon than those made from wheat. Hops also contain more silicon than cereals, but they contribute less to the overall silicon content of beer because they are used in smaller quantities.
In addition to the benefits of these specific nutrients, beer can also contribute to a healthy diet by providing calories and carbohydrates. However, it's important to note that beer is not a significant source of essential vitamins and minerals, and most people can get enough of these nutrients from a balanced diet without consuming beer.
Hard Seltzer vs Beer: Which is the Healthier Choice?
You may want to see also

It can help improve sleep
Non-alcoholic beer can be a great way to improve your sleep. While alcohol is known to make you sleepy, it often results in fragmented sleep in the second half of the night as its effects wear off. It can also make your breathing more laboured, and worsen obstructive sleep apnea. So, opting for a non-alcoholic beer is a better choice for a good night's sleep.
The hops in non-alcoholic beer act on the central nervous system by increasing the levels of GABA, a known inhibitory neurotransmitter. Hops also contain a mild sedative called Lupulin, which can help you relax and unwind before bed. A study published in Public Library of Science One (PLoS One) found that drinking non-alcoholic beer with dinner may help you fall asleep faster, sleep more soundly, and reduce anxiety. The study involved a group of Spanish researchers who studied 17 healthy nurses working rotating or night shifts. During a 14-day period, the nurses drank one 12-ounce bottle of non-alcoholic beer with dinner and their sleep quality was assessed using actigraphy, a motion sensor used to analyse sleep. The data was then compared to that obtained prior to the study period. The researchers found that drinking non-alcoholic beer reduced the time it took the nurses to fall asleep and reduced their movements during sleep. Their anxiety levels also decreased.
Another study conducted by the University of Extremadura Neuroimmunophysiology and Chrononutrition Research Group found that drinking non-alcoholic beer improved sleep quality in a group of 30 university students. The study took place over a period of 3 weeks, with the first 7 days used as a control. During the following 14 days, the students ingested one beer during dinner. The results revealed that subjective sleep quality improved, with a decrease in sleep latency and an improvement in the global score of quality of sleep.
In addition to improving sleep quality, non-alcoholic beer can also help reduce stress and anxiety. A study found that drinking 330 ml (around 11 oz) of non-alcoholic beer per night for two weeks helped reduce feelings of stress. So, if you're looking to unwind after a long day, a non-alcoholic beer might be a good choice.
Beer Bread: Healthy or Harmful?
You may want to see also

It may reduce stress and anxiety
Non-alcoholic beer has been shown to have a positive impact on stress and anxiety. The hops in non-alcoholic beer have sedative properties, which can help to reduce anxiety and improve sleep quality. A study of female nurses working night shifts found that drinking non-alcoholic beer with dinner for two weeks reduced anxiety and improved sleep. Similarly, a study of students under stress from exams found that drinking one non-alcoholic beer with dinner for two weeks reduced anxiety.
Non-alcoholic beer may also help to reduce stress and anxiety by removing alcohol, which is a toxin that can negatively impact mental health. Alcohol can provide short-term relief from anxiety but can lead to long-term substance problems and worsen anxiety over time. Non-alcoholic beer provides a way to enjoy the taste of beer without the negative effects of alcohol.
In addition to reducing stress and anxiety, non-alcoholic beer has several other potential health benefits. It is lower in calories than regular beer and can help with hydration, making it a good option for athletes. It also contains essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, including B vitamins, calcium, potassium, and iron.
Overall, non-alcoholic beer can be a healthier alternative to regular beer and may help to reduce stress and anxiety. However, it is important to note that non-alcoholic beer still contains some calories and carbohydrates, so it should be consumed in moderation as part of a balanced diet.
Ranch Water vs Beer: Which Drink is Healthier?
You may want to see also

It can be a good recovery drink after exercise
Non-alcoholic beer has been found to be a good recovery drink after exercise. It has been deemed a reasonable recovery drink by Johannes Scherr, the chief physician and head of the University Center for Prevention and Sports Medicine at Balgrist University Hospital at the University of Zurich. This is because non-alcoholic beer can help maintain electrolyte homeostasis during exercise. It provides water, polyphenols, and carbohydrates, which aid metabolic recovery.
Non-alcoholic beer is also a better choice than regular beer or sports drinks for performance, recovery, and overall health. Full-alcohol beer is a diuretic, which is counterproductive for rehydration after exercise. Research has shown that drinking beer after a workout increases urine production compared to drinking water or a sports drink. Alcohol can also affect how well our muscles strengthen and grow after exercise and, unsurprisingly, impairs reaction time and balance.
Non-alcoholic beer, on the other hand, has been found to be useful for hydration. In a 2016 study, male athletes who drank non-alcoholic beer 45 minutes before a workout were less dehydrated afterward than if they had drunk beer, and their hydration levels were similar to those of athletes who drank water. The non-alcoholic beer group also had a better ratio of sodium to potassium.
In addition, non-alcoholic beer has been linked to fewer colds and less inflammation. A 2012 study found that the incidence of upper respiratory tract infections was 3.25 times lower among those who drank non-alcoholic beer compared to a control group. The beer drinkers also showed lower markers of inflammation and improved immune response in their blood. These benefits were attributed to the polyphenols in beer, which have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.
However, it is important to note that non-alcoholic beers still contain some alcohol, ranging from 0.0% to 0.5% ABV. Additionally, these beverages contain calories, typically around 50 to 90 per can or bottle, which is a consideration for weight control. Finally, beer, even if non-alcoholic, can cause gastrointestinal discomfort during exercise due to its carbonation.
Beer for Hair: Healthy Shine or Foamy Disaster?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Non-alcoholic beer is healthier than regular beer as it contains fewer calories and less alcohol. However, it is not necessarily good for you as it still contains calories, carbohydrates, and trace amounts of alcohol.
No, it is recommended that pregnant people avoid consuming non-alcoholic beers as they may still contain unsafe amounts of alcohol.
Yes, non-alcoholic beer contains essential vitamins, minerals, fiber, and antioxidants, including B vitamins, calcium, potassium, zinc, selenium, and iron. It can also improve bone density, promote sleep, reduce stress, and improve circulation.
Yes, non-alcoholic beer is a great way to reduce your alcohol intake while still enjoying the taste and experience of beer. It is also a better option if you are the designated driver as it has less impact on blood alcohol concentration.
Yes, non-alcoholic beer may trigger cravings and a relapse in people recovering from alcohol use disorder. It is also important to note that non-alcoholic beer should be consumed in moderation as it is high in carbs and may lead to weight gain and other health issues.







