The fascinating process of how polar beers maintain their pristine cleanliness involves a unique mechanism. Polar beers possess an extraordinary ability to self-clean, a phenomenon that captivates both scientists and beer enthusiasts alike. This natural cleaning process is a result of the beer's composition and the environment in which it is stored. The beer's ingredients, including its proteins and natural preservatives, create a protective layer that prevents dirt and impurities from adhering to the surface. Additionally, the low-temperature environment of the beer's storage area contributes to its self-cleaning properties, as it helps maintain the beer's freshness and purity. This intriguing ability not only ensures the beer's quality but also adds to the intrigue surrounding the fascinating world of polar beers.
What You'll Learn
- Microbiome: Polar beers harness a unique microbiome to self-clean
- Enzymatic Activity: Enzymes break down contaminants, aiding in natural cleaning
- pH Regulation: Polar beers maintain optimal pH for self-purification
- Osmotic Pressure: Osmotic pressure helps expel impurities and maintain purity
- Biological Barriers: Specialized cells and membranes protect against contaminants

Microbiome: Polar beers harness a unique microbiome to self-clean
The fascinating world of beer brewing has unveiled a remarkable innovation in the realm of polar beers, showcasing their ability to self-clean through a unique microbial ecosystem. This natural process is a testament to the intricate relationship between beer and its microbial companions. Polar beers, known for their refreshing crispness, owe their self-cleaning properties to a carefully curated microbiome.
At the heart of this process lies a diverse community of microorganisms, primarily bacteria, that inhabit the beer's environment. These microbes form a symbiotic relationship with the beer, playing a crucial role in its fermentation and aging. The key to self-cleaning lies in the beer's ability to produce and maintain a balanced pH level. Certain bacteria in the microbiome are responsible for this, creating an environment that is inhospitable to harmful pathogens. These beneficial bacteria produce organic acids, such as lactic acid, which lower the pH, making the beer more acidic. This acidic environment acts as a natural preservative, inhibiting the growth of bacteria that could cause spoilage.
The beer's microbiome is a dynamic system, constantly evolving and adapting. Brewers carefully select and introduce specific strains of bacteria to create a desired flavor profile and enhance the beer's natural cleaning abilities. This process is akin to cultivating a garden, where specific plants are nurtured to thrive and outcompete unwanted weeds. By encouraging the growth of beneficial bacteria, polar beers can maintain their quality and freshness over extended periods.
This natural self-cleaning mechanism is a result of the beer's unique brewing process and the careful management of the microbial environment. The beer's journey from malt to mug involves a series of steps where different microorganisms contribute to its transformation. During fermentation, yeast converts sugars into alcohol and carbon dioxide, while bacteria play a role in breaking down complex compounds, adding complexity to the beer's flavor. The aging process further refines the beer, allowing the microbiome to mature and stabilize.
In summary, polar beers' ability to self-clean is a fascinating aspect of brewing science. It highlights the importance of the beer's microbiome, a diverse and dynamic ecosystem, in maintaining quality and freshness. By harnessing the power of these microscopic organisms, brewers can create beers that not only taste exceptional but also have an inherent ability to preserve their own purity. This natural process is a testament to the intricate balance of nature and the art of crafting beverages that delight the senses.
Exploring the World of Lagers: Top 5 Examples and Their Unique Flavors
You may want to see also

Enzymatic Activity: Enzymes break down contaminants, aiding in natural cleaning
The process of self-cleaning in polar beers, a fascinating phenomenon, is largely attributed to the unique enzymatic activity present within these organisms. Polar beers, often found in cold environments, have evolved to possess specialized enzymes that play a crucial role in their survival and maintenance. These enzymes are the key to their remarkable ability to clean and maintain their internal environment.
Enzymatic activity is a natural process where specific proteins, known as enzymes, catalyze biochemical reactions. In the context of polar beers, these enzymes are responsible for breaking down and neutralizing various contaminants that may be present in their habitat. The process begins with the secretion of these enzymes, which are then released into the surrounding environment. These enzymes act as powerful catalysts, facilitating the breakdown of organic matter and inorganic compounds. For instance, they can degrade complex molecules like proteins, lipids, and even certain types of pollutants, into simpler, less harmful substances.
One of the most significant advantages of this enzymatic process is its natural and environmentally friendly nature. Unlike chemical cleaning agents, which often require harsh conditions and can be detrimental to the ecosystem, enzymatic activity uses biological catalysts that are gentle and efficient. These enzymes specifically target and break down contaminants, ensuring that the beer's internal environment remains clean and healthy. This natural cleaning mechanism is a testament to the beer's adaptability and survival strategies in harsh conditions.
The specific enzymes involved in this process are tailored to the beer's unique needs. For example, lipases are enzymes that break down fats and oils, which could be harmful if they accumulate. Proteases target proteins, preventing them from forming harmful clumps. Additionally, certain polar beers may possess enzymes capable of degrading specific pollutants, ensuring their survival in environments with varying levels of contamination. This adaptability is a key factor in the beer's longevity and ability to thrive in diverse habitats.
In summary, the self-cleaning mechanism of polar beers is a remarkable example of nature's ingenuity. Through the release of specialized enzymes, these organisms can effectively break down contaminants, ensuring their internal environment remains clean and functional. This natural process not only contributes to the beer's survival but also highlights the importance of enzymatic activity in maintaining ecological balance. Understanding these processes can provide valuable insights into the field of biology and potentially inspire more sustainable cleaning methods.
Fermenting Beer: Unraveling the Mystery of Krausen Formation
You may want to see also

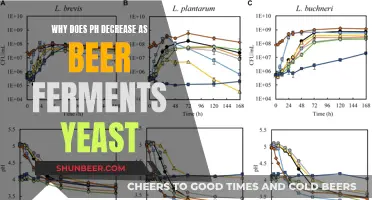
pH Regulation: Polar beers maintain optimal pH for self-purification
The self-purification process of polar beers is a fascinating natural phenomenon, and pH regulation plays a crucial role in this unique cleaning mechanism. Polar beers, also known as glacial beers, are a rare and intriguing variety of beer, typically brewed with ingredients sourced from the Arctic regions. These beers have an extraordinary ability to maintain their purity and quality without the need for extensive filtration or chemical treatments, which is a result of the natural pH balance they achieve.
PH, a measure of the acidity or alkalinity of a substance, is a critical factor in the beer-making process. In the context of polar beers, maintaining the optimal pH is essential for their self-purification properties. The pH level of these beers is carefully regulated to create an environment that encourages the growth of beneficial microorganisms while inhibiting harmful ones. This natural pH regulation is a key aspect of the beer's ability to clean itself.
The process begins with the selection of high-quality, locally sourced ingredients. Polar beers often incorporate glacial water, which has a unique mineral composition that contributes to the beer's purity. The water's pH is naturally slightly alkaline, providing an ideal starting point for the brewing process. Brewers then carefully adjust the pH to a specific range, typically around 6.5 to 7.0, which is slightly above neutral. This slightly alkaline pH is crucial as it creates an environment that promotes the growth of beneficial bacteria and yeast, which are essential for the beer's flavor and clarity.
During the brewing process, the regulated pH ensures that the beer's natural ingredients undergo a series of chemical reactions. Enzymes and yeast work in harmony to break down complex sugars and starches, producing alcohol and carbon dioxide. This process, known as fermentation, is highly dependent on the pH level. The optimal pH range encourages the fermentation process to occur efficiently, resulting in a clean and crisp beer with a well-balanced flavor profile.
Moreover, the pH regulation in polar beers extends beyond the brewing process. After bottling or packaging, the beer's pH continues to play a vital role in its self-purification. The slightly alkaline environment inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria and prevents spoilage. This natural preservation method ensures that polar beers remain fresh and pure, even without the need for additional preservatives. The pH regulation is a key factor in maintaining the beer's quality and longevity, allowing it to clean and preserve itself over time.
In summary, pH regulation is a critical aspect of how polar beers clean themselves. By maintaining an optimal pH range, these beers create an environment that fosters beneficial microorganisms and efficient fermentation. This natural process results in a pure, flavorful beer that requires minimal external intervention. Understanding and appreciating the role of pH in polar beers can provide valuable insights into the art of brewing and the unique characteristics of these remarkable beverages.
Uncovering the Lag: Two Products Behind Beer's Delayed Delivery
You may want to see also

Osmotic Pressure: Osmotic pressure helps expel impurities and maintain purity
Osmotic pressure is a fundamental concept in understanding how polar beers, or any polar substances, can be effectively cleaned and purified. This process is particularly crucial in the context of beer brewing, where maintaining purity and removing impurities is essential for producing high-quality beverages. Here's how osmotic pressure plays a vital role in this cleaning process:
In the context of beer, osmotic pressure refers to the pressure exerted by the solvent (usually water) on a semipermeable membrane that separates the beer from its impurities. Polar beers, such as lagers and pilsners, have a unique molecular structure that allows them to exhibit this phenomenon. The beer's molecules, being polar, have a slightly positive charge on one end and a slightly negative charge on the other, which is crucial for the cleaning process.
When a polar beer is exposed to a concentrated solution of impurities, such as a salt or sugar solution, the osmotic pressure comes into play. The beer's molecules, being attracted to the water molecules in the concentrated solution, start to move towards the solution. This movement is driven by the difference in concentration across the semipermeable membrane. As a result, the beer's impurities, which are not as easily attracted to water, begin to separate from the beer itself. This process effectively cleans the beer by removing unwanted particles and substances.
The key advantage of using osmotic pressure is its ability to selectively expel impurities while retaining the desired components of the beer. The semipermeable membrane allows water molecules to pass through, but it selectively blocks larger molecules and impurities. This selective permeability ensures that the beer's essential flavor compounds, enzymes, and other desirable substances remain intact while impurities are removed.
Furthermore, osmotic pressure can be controlled and manipulated to achieve specific cleaning goals. By adjusting the concentration of the impurity solution, the pressure, and the duration of the process, brewers can customize the cleaning procedure. This level of control is essential for producing beers with consistent quality and purity. For instance, a brief osmotic pressure treatment might be used to quickly remove surface contaminants, while a longer process could be employed to address more deeply embedded impurities.
In summary, osmotic pressure is a powerful tool in the purification of polar beers, leveraging the unique properties of polar molecules and their interaction with water. This method ensures that the final product is free from unwanted substances, contributing to the overall quality and taste of the beer. Understanding and utilizing osmotic pressure allows brewers to maintain the integrity of their beers and create beverages that meet the highest standards of purity and flavor.
San Miguel Beer: Unraveling the Lager-Ale Mystery
You may want to see also

Biological Barriers: Specialized cells and membranes protect against contaminants
The human body employs an intricate system of biological barriers to protect itself from contaminants, and this is particularly evident in the unique mechanism of polar bears' fur. While the question of "how polar beers clean themselves" might seem to be a typo, it's an intriguing inquiry into the natural world's defense mechanisms. However, I assume you meant to ask about polar bears, and I'll provide an answer based on that assumption.
Polar bears, native to the Arctic region, have evolved remarkable adaptations to survive in their harsh environment. Their fur is a prime example of a biological barrier that plays a crucial role in their survival. The fur is composed of a dense layer of hollow, translucent hair, which is covered by a finer down. This structure creates a barrier that is both waterproof and insulating, allowing the bear to thrive in freezing temperatures.
The key to this barrier's effectiveness lies in its specialized cells and membranes. The fur's structure is such that it traps air, creating a layer of insulation. This air layer is protected by a unique cellular arrangement. The cells in the fur are tightly packed, forming a continuous membrane that prevents water and other contaminants from penetrating. The membrane's composition is such that it repels water, ensuring that the bear's skin remains dry and clean.
The process of cleaning and maintaining this biological barrier is an inherent part of the polar bear's physiology. As the bear moves through its environment, the fur's natural oils and dirt are kept at bay. The fur's structure and the bear's natural grooming behavior further contribute to this self-cleaning mechanism. Polar bears often use their paws to wipe their fur, removing any excess dirt and maintaining the integrity of the protective layer.
Additionally, the specialized cells in the fur's base layer play a vital role. These cells are designed to regenerate and replace damaged or worn-out fur, ensuring the barrier remains effective over time. This cellular turnover is a natural process that allows the polar bear to adapt to changing environmental conditions and maintain its protective shield. The combination of the fur's structure, the bear's grooming behavior, and the specialized cellular functions creates a robust biological barrier, showcasing the wonders of nature's defense systems.
Uncover the Secrets of the Classic AA Lager Beer
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Polar beers, a unique and innovative beverage concept, employ a self-cleaning mechanism that is both fascinating and efficient. These beers utilize a specialized brewing process that incorporates a layer of protective wax on the inner surface of the beer container. This wax acts as a barrier, preventing any residue or contaminants from adhering to the glass. As a result, the beer remains clean and clear, providing a pristine drinking experience.
The self-cleaning ability of polar beers is attributed to the unique composition of the wax layer. This wax is designed to be non-stick and food-grade, ensuring it is safe for consumption. When the beer is poured, the liquid creates a temporary film on the surface, which, when combined with the non-stick wax, causes any potential contaminants to wash away as the beer is consumed. This process effectively keeps the beer clean and maintains its clarity.
The self-cleaning mechanism is designed to work seamlessly with various beer styles and ingredients. The protective wax layer is applied uniformly, ensuring that the beer's flavor and quality are not compromised. Whether it's a crisp lager, a rich stout, or a fruity wheat beer, the self-cleaning process remains effective. The key factor is the quality of the wax and its ability to create a non-stick surface, which is consistent across different beer varieties.
Absolutely! The self-cleaning technology of polar beers has potential environmental advantages. By reducing the need for frequent cleaning and maintenance, this process can minimize water usage and chemical cleaning agents typically required in traditional beer production. Additionally, the non-stick wax layer may contribute to a more sustainable approach to beverage packaging, as it can potentially reduce waste and the use of single-use cleaning materials.